
There are security considerations that we should be aware of when we distribute workbooks through tableau reader. Tableau Reader is intended to make your workbooks available to anyone- even those that do not have a Tableau licensed product.
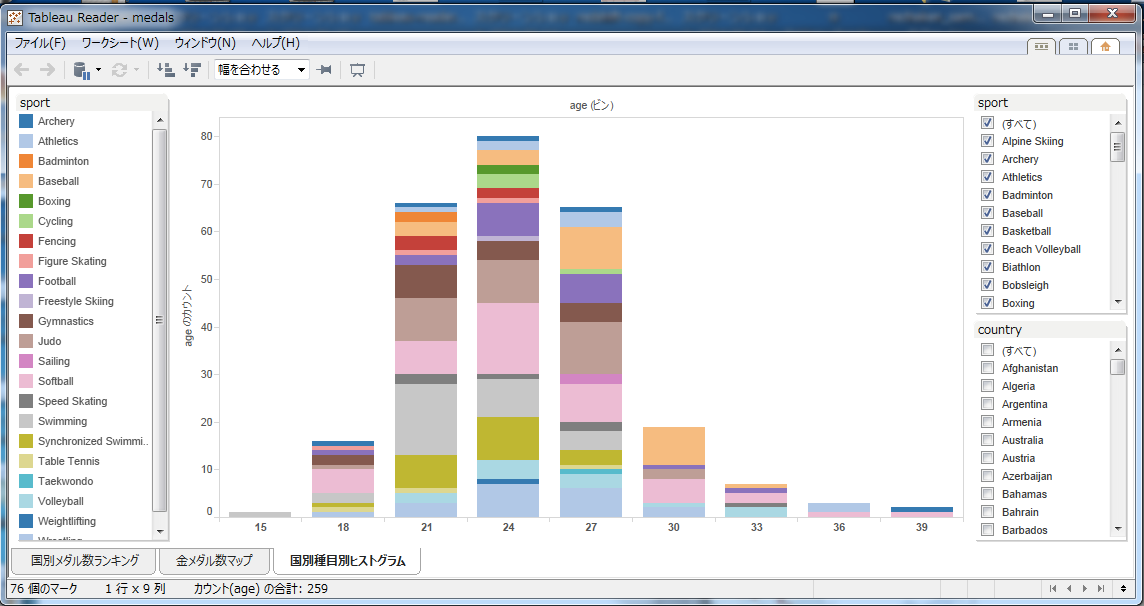
Tableau Packaged Workbooks (.twbx) require local file sources such as Excel, Access, text files(.csv.txt, etc), Tableau data extract files(.tde)ģ More on Tableau Reader If the data source for the workbook we want to share with Tableau Reader comes from a server-based database (SQL Server, Teradata, Oracle, etc.), we must extract the source data first- saving extracted data as a Tableau Data Extract-then save the workbook as a Tableau Packaged Workbook. Distributing content with Tableau Reader requires that you save the Tableau workbook file as a packaged workbook.
TABLEAU READER 9.1 FREE
But, when we want to share a workbook with someone that doesn’t have access to Tableau Server, Tableau Reader provides a free alternative. Tableau Server Nithyamoorthy S Core Mind TechnologiesĢ Tableau Reader The most secure way to distribute Tableau workbooks is via Tableau Server. Adjust font size and style as appropriate.Presentation on theme: "Nithyamoorthy S Core Mind Technologies"- Presentation transcript: Add chart/map titles (if you wish), shorten and clarify axis labels, and simplify tooltips (Figure 9.8). The last step before adding our visualizations to a dashboard is to clean up their design. Your color schemes (map and graph) should be equivalent, as we are only going to create one legend for our dashboard. Edit your color scheme so that it matches the one from your map. Once we've created a graph, it's time to add color! Drag the same data measure from the sidebar to the Color box in the Marks section to color your bars according to that data-as the length of the bar already represents this value, adding color here is called dual encoding. You can change how your measures are calculated by clicking on the colored green oval "pill" of the measure you want to change.
If you had an Excel file with multiple rows for each state, Tableau would sum those values and display that calculated value - you may, in that case, want to display the average in each state instead. Since in our data we have only one value per state, the sum is equivalent to the original value. You may notice that when you add your measure (here, % female 85+) to a graph/chart/map in Tableau, the default measurement is SUM (see Figure 9.7). You may choose to map another geography (e.g., counties, census tracts, block groups) for your own Lab, but using one of these geographies is more advanced and will not be covered here. The most important component of this Excel sheet is the State column-Tableau will automatically recognize and map several geographies, such as States, Countries, Zipcodes, and Coordinates (lat/long). If you're not sure what data to use for your own project, the ACS is a good place to start. It was created by making minor edits to a CSV file downloaded from the US Census Bureau's American Community Survey (ACS). This file has multiple fields (columns) of data for each state in the United States. To begin, open the Age_andSex_AFF_ACS_2017 Excel file. The final result will be a Tableau Story similar to the one about Airbnb data in Portland we discussed in Lesson 9. In this lab, we will design an interactive geovisualization with Tableau.

In Part 1, follow these steps to create the example, Tableau Story.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
